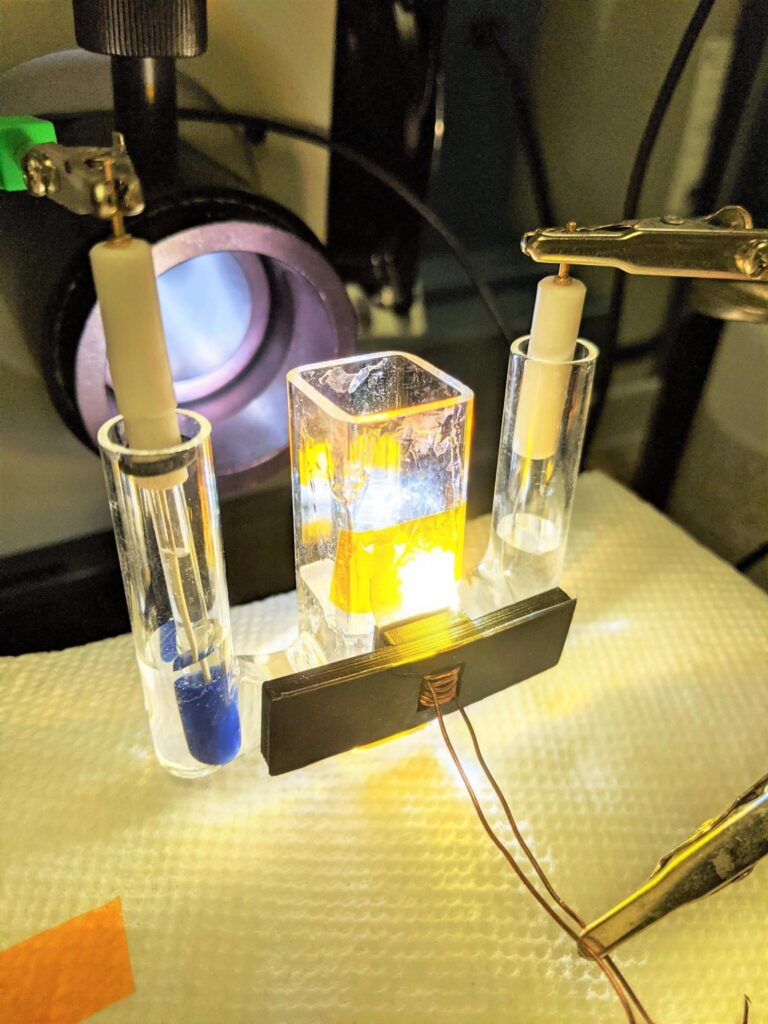
For decades, researchers around the world have searched for ways to use solar power to generate the key reaction for producing hydrogen as a clean energy source — splitting water molecules to form hydrogen and oxygen. However, such efforts have mostly failed because doing it well was too costly, and trying to do it at a low cost led to poor performance.
Now, researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have found a low-cost way to solve one half of the equation, using sunlight to efficiently split off oxygen molecules from water. The finding, published recently in Nature Communications, represents a step forward toward greater adoption of hydrogen as a key part of our energy infrastructure.
As early as the 1970s, researchers were investigating the possibility of using solar energy to generate hydrogen. But the inability to find materials with the combination of properties needed for a device that can perform the key chemical reactions efficiently has kept it from becoming a mainstream method.
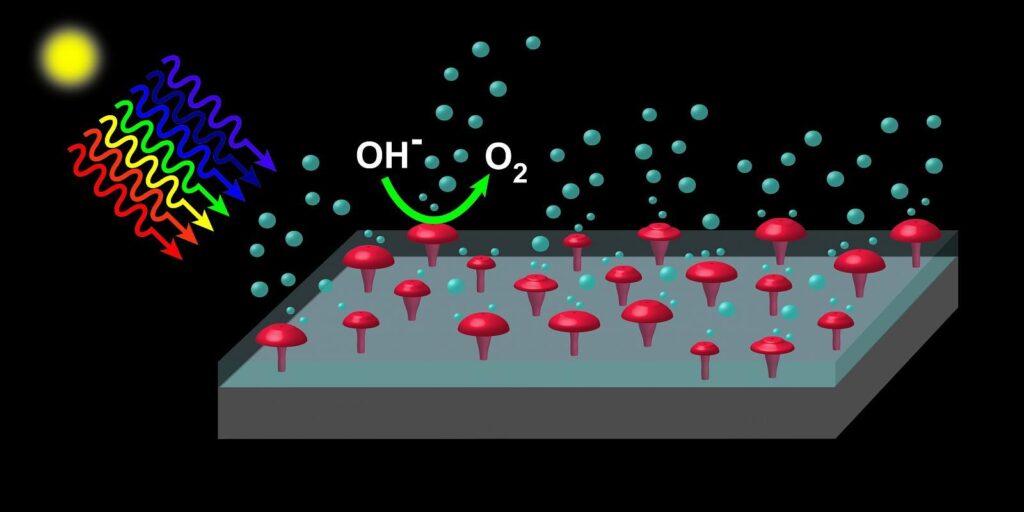
“You need materials that are good at absorbing sunlight and, at the same time, don’t degrade while the water-splitting reactions take place,” said Edward Yu, a professor in the Cockrell School’s Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. “It turns out materials that are good at absorbing sunlight tend to be unstable under the conditions required for the water-splitting reaction, while the materials that are stable tend to be poor absorbers of sunlight. These conflicting requirements drive you toward a seemingly inevitable tradeoff, but by combining multiple materials — one that efficiently absorbs sunlight, such as silicon, and another that provides good stability, such as silicon dioxide — into a single device, this conflict can be resolved.”
However, this creates another challenge — the electrons and holes created by the absorption of sunlight in silicon must be able to move easily across the silicon dioxide layer. This usually requires the silicon dioxide layer to be no more than a few nanometers, which reduces its effectiveness in protecting the silicon absorber from degradation.
The key to this breakthrough came through a method of creating electrically conductive paths through a thick silicon dioxide layer that can be performed at low cost and scaled to high manufacturing volumes. To get there, Yu and his team used a technique first deployed in the manufacturing of semiconductor electronic chips. By coating the silicon dioxide layer with a thin film of aluminum and then heating the entire structure, arrays of nanoscale “spikes” of aluminum that completely bridge the silicon dioxide layer are formed. These can then easily be replaced by nickel or other materials that help catalyze the water-splitting reactions.
When illuminated by sunlight, the devices can efficiently oxidize water to form oxygen molecules while also generating hydrogen at a separate electrode and exhibit outstanding stability under extended operation. Because the techniques employed to create these devices are commonly used in manufacturing semiconductor electronics, they should be easy to scale for mass production.
The team has filed a provisional patent application to commercialize the technology.
Improving the way hydrogen is generated is key to its emergence as a viable fuel source. Most hydrogen production today occurs through heating steam and methane, but that relies heavily on fossil fuels and produces carbon emissions.
There is a push toward “green hydrogen” which uses more environmentally friendly methods to generate hydrogen. And simplifying the water-splitting reaction is a key part of that effort.
Hydrogen has the potential to become an important renewable resource with some unique qualities. It already has a major role in significant industrial processes, and it is starting to show up in the automotive industry. Fuel cell batteries look promising in long-haul trucking, and hydrogen technology could be a boon to energy storage, with the ability to store excess wind and solar energy produced when conditions are ripe for them.
Going forward, the team will work to improve the efficiency of the oxygen portion of water-splitting by increasing the reaction rate. The researchers’ next major challenge is then to move on to the other half of the equation.
“We were able to address the oxygen side of the reaction first, which is the more challenging part, ” Yu said, “but you need to perform both the hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions to completely split the water molecules, so that’s why our next step is to look at applying these ideas to make devices for the hydrogen portion of the reaction.”
Reference: “Scalable, highly stable Si-based metal-insulator-semiconductor photoanodes for water oxidation fabricated using thin-film reactions and electrodeposition” by Soonil Lee, Li Ji, Alex C. De Palma, and Edward T. Yu, 25 June 2021, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24229-y
This research was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation through the Directorate for Engineering and the Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSEC) program. Yu worked on the project with UT Austin students Soonil Lee and Alex De Palma, along with Li Ji, a professor at Fudan University in China.
REposted from scitechdaily.com
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .